Course Content
-
Pediatric Heart Failure: “How to approach the management of Pediatric Heart Failure” Understanding heart failure: the basics in pediatric heart failure and congenital heart diseases. Basics of treatment and decision making in clinic cases
- Introduction. Definition of Heart Failure
- Etiology of Heart Failure in pediatric age
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
- Heart Failure in Congenital Heart Disease
- Natriuretic peptid system
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure
- Signs and Symptoms in pediatric age
- Classification of severity in pediatric Heart Failure
- Different forms of cardiomyopathies: “Diagnostic techniques and treatments”
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Non-compaction Cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- Evaluation Cardiomyopathies and Genetics
- Evaluation Quiz
- Arrhythmias in Pediatric Heart Failure: EKG abnormalities
- Indications ICD in adults and pediatric age
- Clinic Cases. Quiz
- Treatment in chronic pediatric Heart Failure
- New treatment: Sacubitril – Valsartan
- New therapies and Experimental
- Summary Pediatric Heart Failure therapies
-
Basic and Advanced Echocardiography in Pediatric Heart Failure Description of basic and advanced echocardiography tools for diagnostic and follow-up of children affected by heart failure
- Journal Club: “Basic and advanced echocardiography in advanced heart failure: an overview”
- LV systolic function
- RV systolic function
- Cardiac Diastolic Function and Diastolic Heart Failure
- Tissue Doppler Imaging (DTI) and diastolic dysfunction
- Summary Echo left diastolic dysfunction
- RV diastolic dysfunction
- Management of pediatric diastolic dysfunction
- Clinic Cases
- dP/dt LV function assessment
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) Doppler Mitral Flow
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) DTI
- Basics of Strain and Strain-rate
- Global longitudinal Strain (GLS)
- Cardiac output assessment by Echo
- Advanced Imaging in Pediatric Heart Failure
- Echocardiography: Apps and webs
- Clinic Cases
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (I) Basic in inmunology and rejection. Indications of pediatric heart transplant and contraindications. Mechanical support in pediatric age. Surgery and perioperative treatment.
- Basis of transplant immunology
- Human leucocytes antigen (HLA)
- Blood group antigen (ABO)
- Graft Rejection
- Donor selection & evaluation
- Tissue typing and cross matching
- Ischemic time and the TransMedics® Organ Care System (OCS™)
- Indications and Contraindications of Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Indications of pediatric Mechanical cardiac support (MCS)
- Types of Devices for pediatric MCS
- VAD selection for pediatric MCS
- Surgery of Heart Transplant in pediatric age and in Congenital heart disease
- Principle Challenge in immunosuppressive therapies
- Induction therapy during surgery, postoperative period and denervated heart
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (II) Basic of immunosuppression treatment. Management of rejection and infections in pediatric heart transplant. Information for patients and relatives. Outcomes of heart transplant and indications of retransplantation
- Basis of immunosuppression therapy
- Risk of infection after transplantation
- Complication of chronic immunosuppression
- Basis of Rejection and assessment
- Endomyocardial biopsy and rejection
- Treatment of humoral and cellular rejection
- Chronic rejection: Coronary Artery Vasculopathy (CAV)
- Clinic follow-up in patient transplanted
- Cardiac Rehabilitation in pediatric heart transplant
- Survival and Causes of death in pediatric heart transplant
- Indications of retransplantation and survival
- Home Care after Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Palliative care in Pediatric Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation
- Future perspectives. Summary
- Clinic cases
-
Final Quizz Congratulations! You finished the course, check your knowledge with this final test
-
Fellow Evaluation Course Evaluation of the cardiac fellows who attended the course in May 2020
Biomarkers in Heart Failure
Biomarkers have established an important role in the diagnosis and prognosis of heart failure in adults and may represent an objective tool to confirm functional status and echocardiographic indices of left ventricular dysfunction in children with HF.
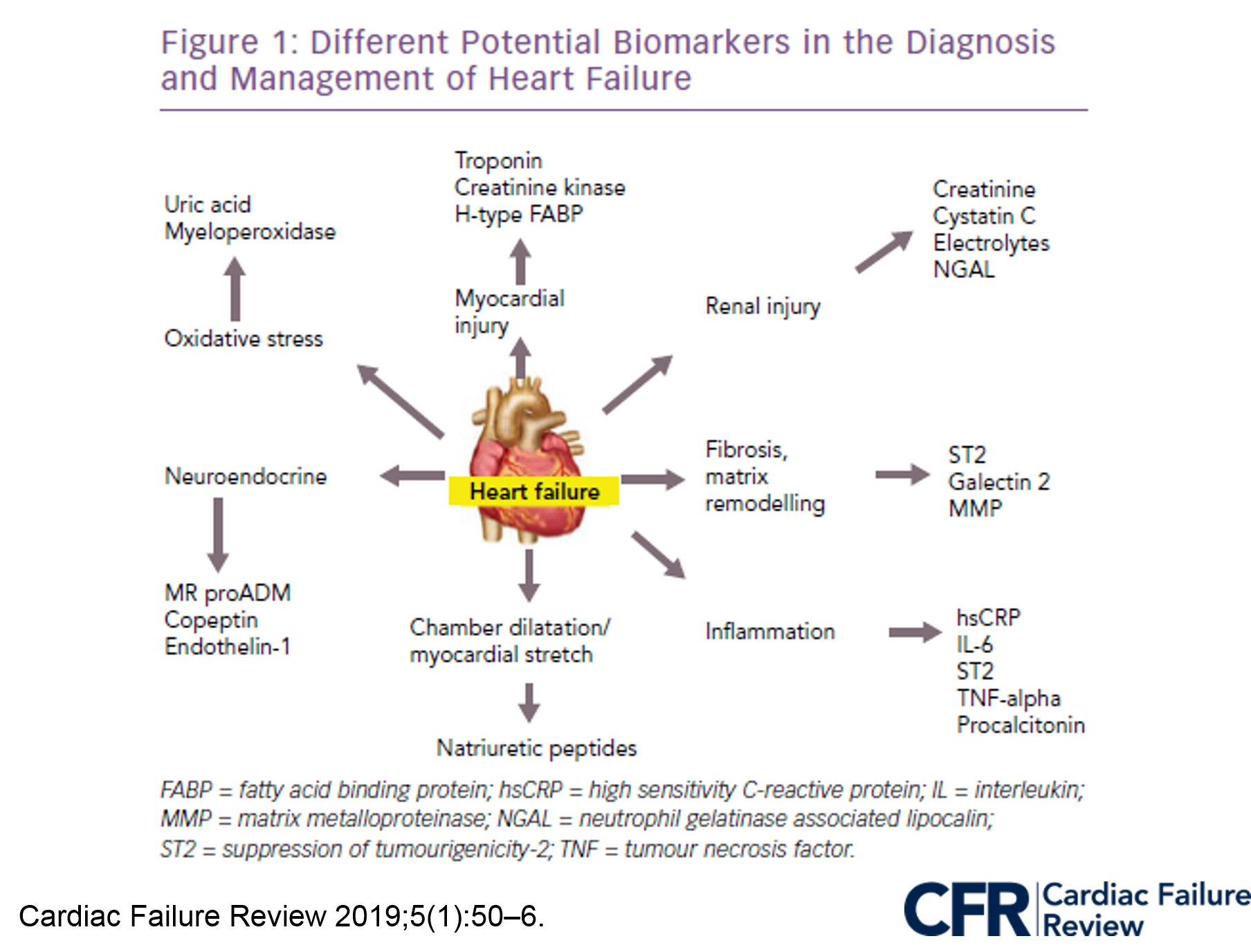
The use of serial BNP or NT-proBNP measurements in children to guide therapeutic intervention or to monitor HF status shows some promise. High-sensitivity C reactive protein, cytokines, cytokine receptors, cardiac troponins and gene expression profiling are all emerging as a useful assessment tools in adults and further study is required to validate the role of these measures in children with HF.
BNP/ NT-proBNP could rule-in or support of initial working diagnosis of HF. BNP is active and has vasodilators effect and its metabolite (Nt-proBNP) inactive. Both increases the levels in acute myocardial dysfunction, declines with treatment or recovery from disease and could rule out respiratory problems instead of HF worsening. Normal levels are BNP < 100 pg/ml and Nt-proBNP < 300 pg/ml. Levels of BNP > 300 pg/ml or Nt-proBNP > 900 pg/ml are the cut-off points for decompensated cases, with a sensitivity and specificity > 85%. The importance in biomarkers clinical use is the trend, more than an isolated measure.
Other biomarkers in HF uses in research and still not clinical applications worlwide:
- ST2 a protein member of the IL-1 receptor family, reflects cardiovascular stress and fibrosis. Currently American College of cardiology Foundation/ American Heart Association Class II recommendation if than ST2 assay is a valuable tool for risk stratification in the setting
- Galectine 3 is secreted by activated macrhophages and causes cardiac fibrosis by proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts. It could be a marker of cardiac remodelling and has strong prognosis value, more than for diagnosis of HF. PRIDE-study in patients adults with HF, high galectine-3 concentrations showed predictive of 60-day mortality. Currently American College of cardiology Foundation/ American Heart Association Class II for risk prediction in HF.


