Course Content
-
Pediatric Heart Failure: “How to approach the management of Pediatric Heart Failure” Understanding heart failure: the basics in pediatric heart failure and congenital heart diseases. Basics of treatment and decision making in clinic cases
- Introduction. Definition of Heart Failure
- Etiology of Heart Failure in pediatric age
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
- Heart Failure in Congenital Heart Disease
- Natriuretic peptid system
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure
- Signs and Symptoms in pediatric age
- Classification of severity in pediatric Heart Failure
- Different forms of cardiomyopathies: “Diagnostic techniques and treatments”
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Non-compaction Cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- Evaluation Cardiomyopathies and Genetics
- Evaluation Quiz
- Arrhythmias in Pediatric Heart Failure: EKG abnormalities
- Indications ICD in adults and pediatric age
- Clinic Cases. Quiz
- Treatment in chronic pediatric Heart Failure
- New treatment: Sacubitril – Valsartan
- New therapies and Experimental
- Summary Pediatric Heart Failure therapies
-
Basic and Advanced Echocardiography in Pediatric Heart Failure Description of basic and advanced echocardiography tools for diagnostic and follow-up of children affected by heart failure
- Journal Club: “Basic and advanced echocardiography in advanced heart failure: an overview”
- LV systolic function
- RV systolic function
- Cardiac Diastolic Function and Diastolic Heart Failure
- Tissue Doppler Imaging (DTI) and diastolic dysfunction
- Summary Echo left diastolic dysfunction
- RV diastolic dysfunction
- Management of pediatric diastolic dysfunction
- Clinic Cases
- dP/dt LV function assessment
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) Doppler Mitral Flow
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) DTI
- Basics of Strain and Strain-rate
- Global longitudinal Strain (GLS)
- Cardiac output assessment by Echo
- Advanced Imaging in Pediatric Heart Failure
- Echocardiography: Apps and webs
- Clinic Cases
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (I) Basic in inmunology and rejection. Indications of pediatric heart transplant and contraindications. Mechanical support in pediatric age. Surgery and perioperative treatment.
- Basis of transplant immunology
- Human leucocytes antigen (HLA)
- Blood group antigen (ABO)
- Graft Rejection
- Donor selection & evaluation
- Tissue typing and cross matching
- Ischemic time and the TransMedics® Organ Care System (OCS™)
- Indications and Contraindications of Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Indications of pediatric Mechanical cardiac support (MCS)
- Types of Devices for pediatric MCS
- VAD selection for pediatric MCS
- Surgery of Heart Transplant in pediatric age and in Congenital heart disease
- Principle Challenge in immunosuppressive therapies
- Induction therapy during surgery, postoperative period and denervated heart
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (II) Basic of immunosuppression treatment. Management of rejection and infections in pediatric heart transplant. Information for patients and relatives. Outcomes of heart transplant and indications of retransplantation
- Basis of immunosuppression therapy
- Risk of infection after transplantation
- Complication of chronic immunosuppression
- Basis of Rejection and assessment
- Endomyocardial biopsy and rejection
- Treatment of humoral and cellular rejection
- Chronic rejection: Coronary Artery Vasculopathy (CAV)
- Clinic follow-up in patient transplanted
- Cardiac Rehabilitation in pediatric heart transplant
- Survival and Causes of death in pediatric heart transplant
- Indications of retransplantation and survival
- Home Care after Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Palliative care in Pediatric Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation
- Future perspectives. Summary
- Clinic cases
-
Final Quizz Congratulations! You finished the course, check your knowledge with this final test
-
Fellow Evaluation Course Evaluation of the cardiac fellows who attended the course in May 2020
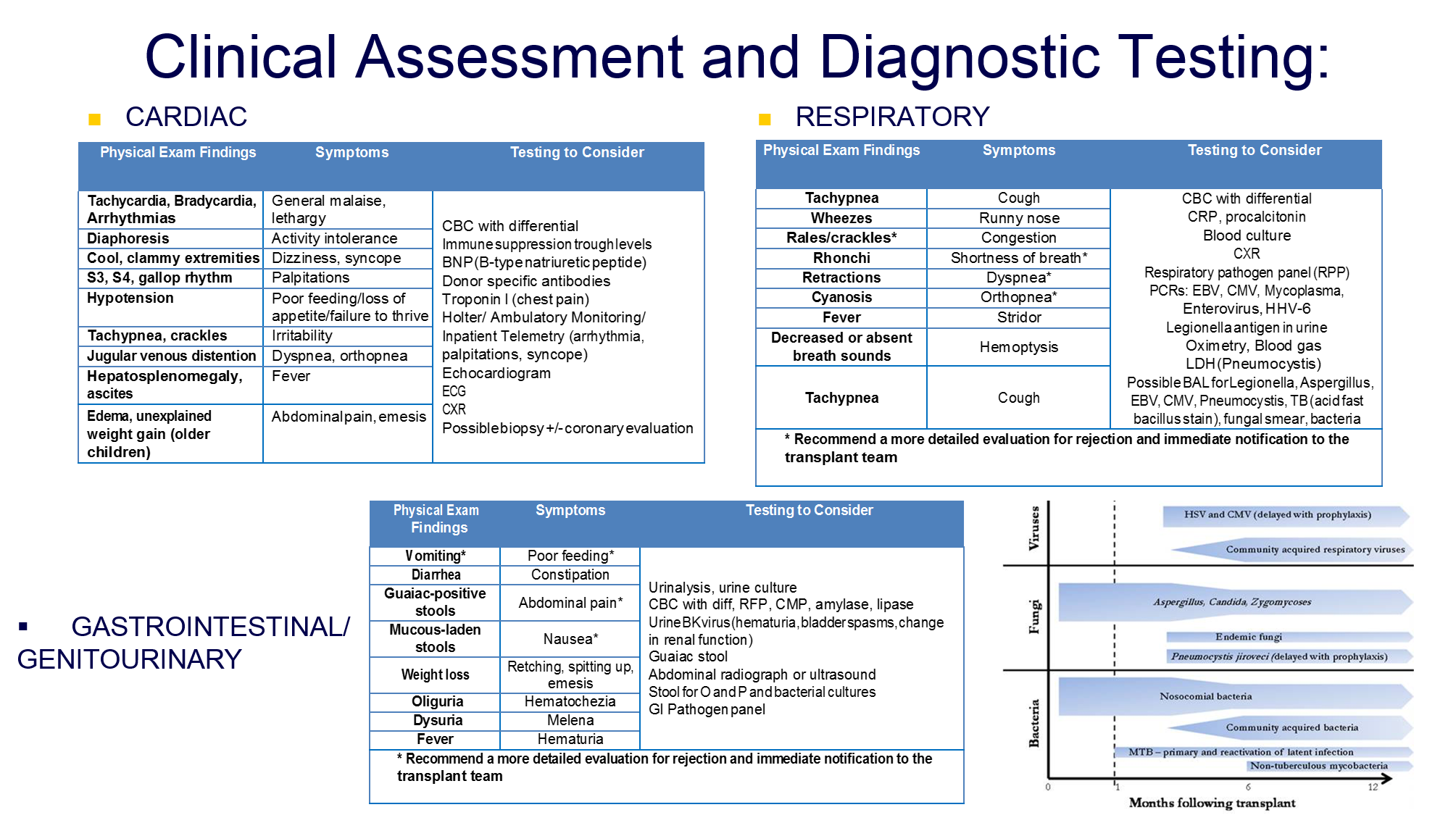
Clinic follow-up in patient transplanted
POST TRANSPLANT CARDIOLOGY EVALUATION
CLINICAL VISIT SCHEDULE
- Every week until 2 months post-transplant:
- THEN every 2 weeks for 2 months
- THEN monthly for 6 months (post-transplant)
- THEN every 4 months after 1-2 years post-transplant
- > 2 years: every 6 months
- If patient is changed to monotherapy after 12-month cath, then patient should return in 1 month for a clinic visit to assess for rejection.
Non-compliance with visits: If the family has not made an appointment, PED Coordinator will call to the family and will be contact to Social Services. If the family fails to appear for more than 1 appointments, social services will evaluate medical neglect and appropriate action will be taken.
ECG/HOLTER MONITORING
- ECG with each clinic visit
- Holter recording at 1st annual visit, repeat annually or biennial if abnormal
- Holter and Stress test annually in patients with CAV
- When clinically indicated based on abnormal ECG, symptoms, etc.
ECHOCARDIOGRAM
- Ecochardiography with each clinic visit (in Echo Lab or Bedside Echo)
- Notify Echolab at first outpatient echo if patient has additional intracardiac defects related to donor organ, or if patient has vascular stenosis or other anatomic abnormalities that require additional imaging (in case of suspiction of rejection, GLS should be carried out).
- Check: biventricular function, size chambers and dimension of septum, mitral regurgitation, mitral flow and DTI mitral (ratio E/E’), pericardial effusion, pulmonary pressure and IVC collapsibility.
ACUTE VISIT
- Acute outpatient visit: initial testing by PED coordinator triaging call
- If patient warrants an Emergency Department visit or is hospitalized with an illness, the patient should have an ECHO and ECG at that time to exclude severe rejection (poor LV function). Rare exception includes patient presentation to ER with obvious alternative illness and no signs/symptoms rejection (as infections, see Table below)
- Additional laboratory work unless patient’s diagnosis is obvious should include: B-type natriuretic peptide, metabolic panel, CBC with differential.