Course Content
-
Pediatric Heart Failure: “How to approach the management of Pediatric Heart Failure” Understanding heart failure: the basics in pediatric heart failure and congenital heart diseases. Basics of treatment and decision making in clinic cases
- Introduction. Definition of Heart Failure
- Etiology of Heart Failure in pediatric age
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
- Heart Failure in Congenital Heart Disease
- Natriuretic peptid system
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure
- Signs and Symptoms in pediatric age
- Classification of severity in pediatric Heart Failure
- Different forms of cardiomyopathies: “Diagnostic techniques and treatments”
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Non-compaction Cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- Evaluation Cardiomyopathies and Genetics
- Evaluation Quiz
- Arrhythmias in Pediatric Heart Failure: EKG abnormalities
- Indications ICD in adults and pediatric age
- Clinic Cases. Quiz
- Treatment in chronic pediatric Heart Failure
- New treatment: Sacubitril – Valsartan
- New therapies and Experimental
- Summary Pediatric Heart Failure therapies
-
Basic and Advanced Echocardiography in Pediatric Heart Failure Description of basic and advanced echocardiography tools for diagnostic and follow-up of children affected by heart failure
- Journal Club: “Basic and advanced echocardiography in advanced heart failure: an overview”
- LV systolic function
- RV systolic function
- Cardiac Diastolic Function and Diastolic Heart Failure
- Tissue Doppler Imaging (DTI) and diastolic dysfunction
- Summary Echo left diastolic dysfunction
- RV diastolic dysfunction
- Management of pediatric diastolic dysfunction
- Clinic Cases
- dP/dt LV function assessment
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) Doppler Mitral Flow
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) DTI
- Basics of Strain and Strain-rate
- Global longitudinal Strain (GLS)
- Cardiac output assessment by Echo
- Advanced Imaging in Pediatric Heart Failure
- Echocardiography: Apps and webs
- Clinic Cases
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (I) Basic in inmunology and rejection. Indications of pediatric heart transplant and contraindications. Mechanical support in pediatric age. Surgery and perioperative treatment.
- Basis of transplant immunology
- Human leucocytes antigen (HLA)
- Blood group antigen (ABO)
- Graft Rejection
- Donor selection & evaluation
- Tissue typing and cross matching
- Ischemic time and the TransMedics® Organ Care System (OCS™)
- Indications and Contraindications of Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Indications of pediatric Mechanical cardiac support (MCS)
- Types of Devices for pediatric MCS
- VAD selection for pediatric MCS
- Surgery of Heart Transplant in pediatric age and in Congenital heart disease
- Principle Challenge in immunosuppressive therapies
- Induction therapy during surgery, postoperative period and denervated heart
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (II) Basic of immunosuppression treatment. Management of rejection and infections in pediatric heart transplant. Information for patients and relatives. Outcomes of heart transplant and indications of retransplantation
- Basis of immunosuppression therapy
- Risk of infection after transplantation
- Complication of chronic immunosuppression
- Basis of Rejection and assessment
- Endomyocardial biopsy and rejection
- Treatment of humoral and cellular rejection
- Chronic rejection: Coronary Artery Vasculopathy (CAV)
- Clinic follow-up in patient transplanted
- Cardiac Rehabilitation in pediatric heart transplant
- Survival and Causes of death in pediatric heart transplant
- Indications of retransplantation and survival
- Home Care after Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Palliative care in Pediatric Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation
- Future perspectives. Summary
- Clinic cases
-
Final Quizz Congratulations! You finished the course, check your knowledge with this final test
-
Fellow Evaluation Course Evaluation of the cardiac fellows who attended the course in May 2020
Tissue Doppler Imaging (DTI) and diastolic dysfunction
Tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) is an echocardiographic technique that uses Doppler principles to measure the velocity of displacement of the annulus (mitral, septal and tricuspid) and reflects the function of longitudinal fibers (mitral – LV function; Septal – global function and tricuspid annulus – RV function). Like many other parameters, it depends upon angle of insonation.
The cardiac cycle is represented by 3 waveforms:
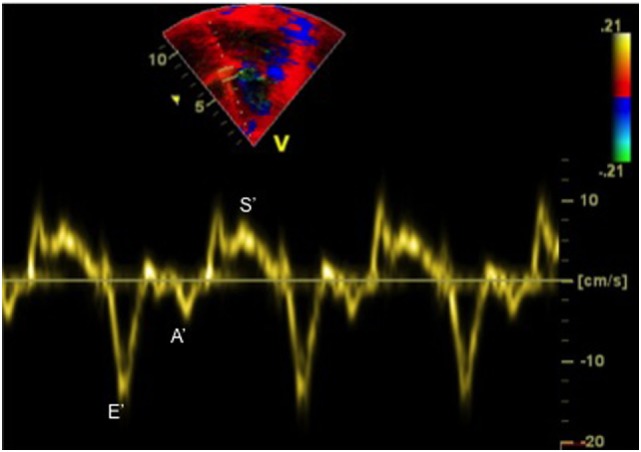
1) S’, systolic myocardial velocity above the baseline as the annulus descends toward the apex;
(2) E’, early diastolic myocardial relaxation velocity below the baseline as the annulus ascends away from the apex;
(3) A’, myocardial velocity associated with atrial contraction
Systolic myocardial velocity (S’) at the lateral mitral annulus is a measure of longitudinal systolic function of LV and is correlated with measurements of LVEF, value < 6cm/sec is correlated with LV impairment function. For RV normal value is > 10cm/sec.
In normal subjects E’ increases as transmitral gradient increases with exertion or increased preload, whereas in patients with impaired myocardial relaxation E’ is reduced at baseline and does not increase as much as in normal subjects with increased preload. Lateral annulus early diastolic velocity is usually higher than septal annulus E’. Decreased E’ is one of the earliest markers for diastolic dysfunction and is present in all stages of diastolic dysfunction. Because E’ velocity remains reduced and mitral E velocity in mitral flow increases with higher filling pressure, the ratio between transmitral E and E’ (E/E’), correlates well with LV filling pressure or pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) in adults (ratio E/E’ > 15 is indicative of increased left heart filling pressure in adults), not demonstrated in children. Adult Guidelines do not readily translate to children.
Figure: E mitral 86cm/sec, E’ 14cm/sec, ratio E/E’ = 86/ 14= 6 (normal ratio)