Course Content
-
Pediatric Heart Failure: “How to approach the management of Pediatric Heart Failure” Understanding heart failure: the basics in pediatric heart failure and congenital heart diseases. Basics of treatment and decision making in clinic cases
- Introduction. Definition of Heart Failure
- Etiology of Heart Failure in pediatric age
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
- Heart Failure in Congenital Heart Disease
- Natriuretic peptid system
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure
- Signs and Symptoms in pediatric age
- Classification of severity in pediatric Heart Failure
- Different forms of cardiomyopathies: “Diagnostic techniques and treatments”
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Non-compaction Cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- Evaluation Cardiomyopathies and Genetics
- Evaluation Quiz
- Arrhythmias in Pediatric Heart Failure: EKG abnormalities
- Indications ICD in adults and pediatric age
- Clinic Cases. Quiz
- Treatment in chronic pediatric Heart Failure
- New treatment: Sacubitril – Valsartan
- New therapies and Experimental
- Summary Pediatric Heart Failure therapies
-
Basic and Advanced Echocardiography in Pediatric Heart Failure Description of basic and advanced echocardiography tools for diagnostic and follow-up of children affected by heart failure
- Journal Club: “Basic and advanced echocardiography in advanced heart failure: an overview”
- LV systolic function
- RV systolic function
- Cardiac Diastolic Function and Diastolic Heart Failure
- Tissue Doppler Imaging (DTI) and diastolic dysfunction
- Summary Echo left diastolic dysfunction
- RV diastolic dysfunction
- Management of pediatric diastolic dysfunction
- Clinic Cases
- dP/dt LV function assessment
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) Doppler Mitral Flow
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) DTI
- Basics of Strain and Strain-rate
- Global longitudinal Strain (GLS)
- Cardiac output assessment by Echo
- Advanced Imaging in Pediatric Heart Failure
- Echocardiography: Apps and webs
- Clinic Cases
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (I) Basic in inmunology and rejection. Indications of pediatric heart transplant and contraindications. Mechanical support in pediatric age. Surgery and perioperative treatment.
- Basis of transplant immunology
- Human leucocytes antigen (HLA)
- Blood group antigen (ABO)
- Graft Rejection
- Donor selection & evaluation
- Tissue typing and cross matching
- Ischemic time and the TransMedics® Organ Care System (OCS™)
- Indications and Contraindications of Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Indications of pediatric Mechanical cardiac support (MCS)
- Types of Devices for pediatric MCS
- VAD selection for pediatric MCS
- Surgery of Heart Transplant in pediatric age and in Congenital heart disease
- Principle Challenge in immunosuppressive therapies
- Induction therapy during surgery, postoperative period and denervated heart
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (II) Basic of immunosuppression treatment. Management of rejection and infections in pediatric heart transplant. Information for patients and relatives. Outcomes of heart transplant and indications of retransplantation
- Basis of immunosuppression therapy
- Risk of infection after transplantation
- Complication of chronic immunosuppression
- Basis of Rejection and assessment
- Endomyocardial biopsy and rejection
- Treatment of humoral and cellular rejection
- Chronic rejection: Coronary Artery Vasculopathy (CAV)
- Clinic follow-up in patient transplanted
- Cardiac Rehabilitation in pediatric heart transplant
- Survival and Causes of death in pediatric heart transplant
- Indications of retransplantation and survival
- Home Care after Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Palliative care in Pediatric Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation
- Future perspectives. Summary
- Clinic cases
-
Final Quizz Congratulations! You finished the course, check your knowledge with this final test
-
Fellow Evaluation Course Evaluation of the cardiac fellows who attended the course in May 2020
Basis of Rejection and assessment
Rejection involves cell- or antibody mediated cardiac injury resulting from recognition of the cardiac allograft as non-self. Risk factors for early rejection include younger recipient age, female sex, female donor, positive cytomegalovirus and EB serologic test results, prior infections, black recipient race, and number of HLA mismatches
- Acute cellular rejection or cell-mediated rejection is a mononuclear inflammatory response, predominantly lymphocytic, directed against the donor heart; It is most common from the first week to several years after transplantation, and it occurs in up to 40% of patients during the first year after surgery
- Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR): patients at greatest risk for antibody-mediated rejection are women and patients with positive crossmatch. It is estimated that significant antibody-mediated rejection occurs in about 7% of patients, but the rate may be as high as 20%
- Chronic rejection
- Late graft failure is an irreversible gradual deterioration of graft function that occurs in many allografts months to years after transplantation
- The current concept suggests that donor heart dysfunction in the chronic stages of maintenance immunosuppression is either related to chronic rejection mediated by antibodies, or a result of progressive graft loss from ischemia
REJECTION ASSESSMENT
- Clinical changes (fever, feeding refusal, fatigue, vomiting, etc.)
- Chest X-ray: Cardiomegaly, evidence of pulmonary congestion/edema
- ECG: Low voltage, arrhythmias (Bradyarrhythmias, heart block, tachyarrhythmias), changes from previous ECG
- Laboratory evaluation: CBC with diff (rising WBC or eosinophilia can indicate rejection), Comprehensive metabolic panel: kidneys/ liver profile, electrolytes, sugar level and acid/base balance (CMP), Nt-proBNP, drug levels (if the timing is appropriate)
- Right/Left heart cath (hemodynamics) and biopsy: need to be determined by treating Transplant MD (particularly helpful when discrepancy between clinical scenario, echocardiographic, ECG abnormalities; and/or when patient’s rejection course is complex, atypical, or not responding to current anti-rejection therapies … after 1 year Chronic Rejection (coronariography to r/o CAV)
- Echocardiography: “remember the donor age”. Data of rejection by Echo:
- Pericardial effusion
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Rapidly increasing LV posterior wall and septal wall thickness
- New tricuspid or mitral valve insufficiency
- Decreasing posterior wall and septal systolic and diastolic function
- Decreasing LV shortening fraction
- Decreasing LV volume (may increase with severe rejection).
- Mitral flow and DTI mitral (ratio E/e’) **
- Impairment GLS
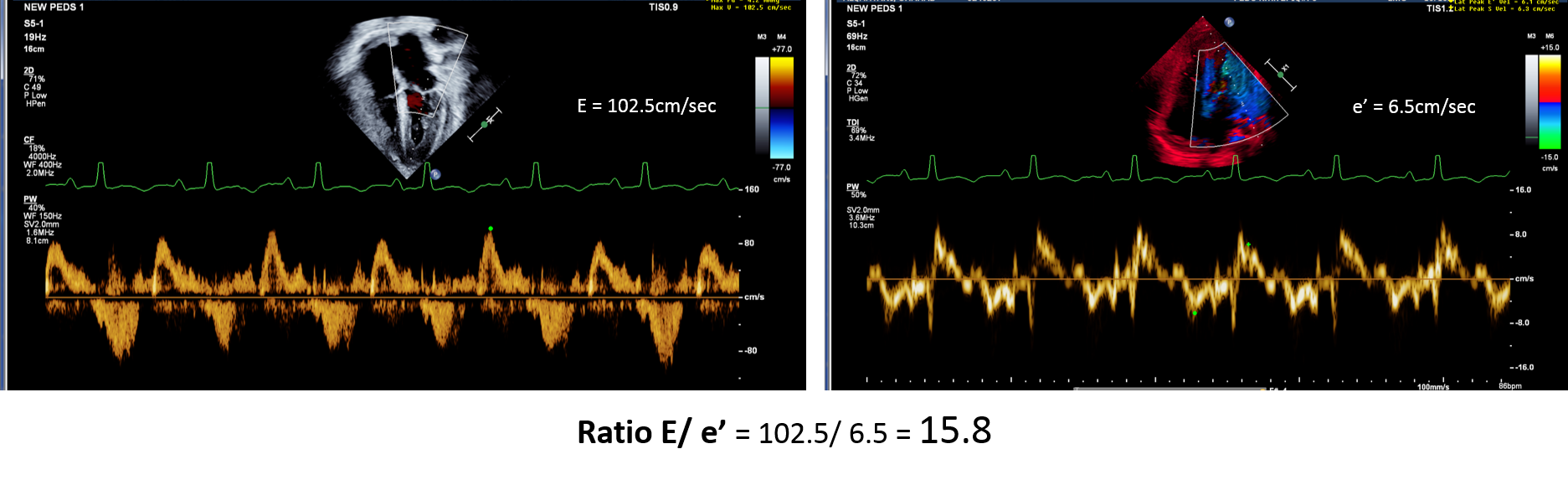
** Ambrosi et al. Predictive value of E/A and E/E’ Doppler indexes for cardiac events in heart transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 2016:30(8):959-63.


